Scaling up stem cell-derived organoid biomanufacturing
Imagine a world where an unlimited number of organs were available for transplantation and research. We could reduce the use of animals in research. When certain organs fail, we could replace them. This may sound like a science fiction trope, but recent technologies in biology and engineering are now making this possible.
Today, microscopic organ models called “organoids” can be produced in Petri dishes. Large quantities of pluripotent stem cells can be grown, and these stem cells can be turned into different types of organoids. Pluripotent stem cells can be derived from a skin or blood sample. So why are we still using animals and cancer cell lines in drug development? Why can’t we transplant these organoids?
Even though organoids are manufactured in several laboratories, protocols vary between and even within each research group. This means that current protocols are typically not sufficiently robust or validated. Most of the time, only tens or hundreds of organoids are produced at a time, whereas nearly a million are needed per patient to treat diabetes, as an example. Quality control also varies greatly from one laboratory to another.
The aim of this project is to bring together several players in Quebec to standardize practices, establish quality measures and robust protocols, and scale up production. Students and staff from 12 labs in Quebec will work together to produce these advanced therapies, while developing unique skills in biomanufacturing of clinical-grade cells. The current project focuses on pancreatic organoids to treat type 1 diabetes, liver organoids to treat liver failure, and brain organoids to study neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease. The long-term vision is to make a wide range of organoids available for clinical and basic research, as well as cell therapy.
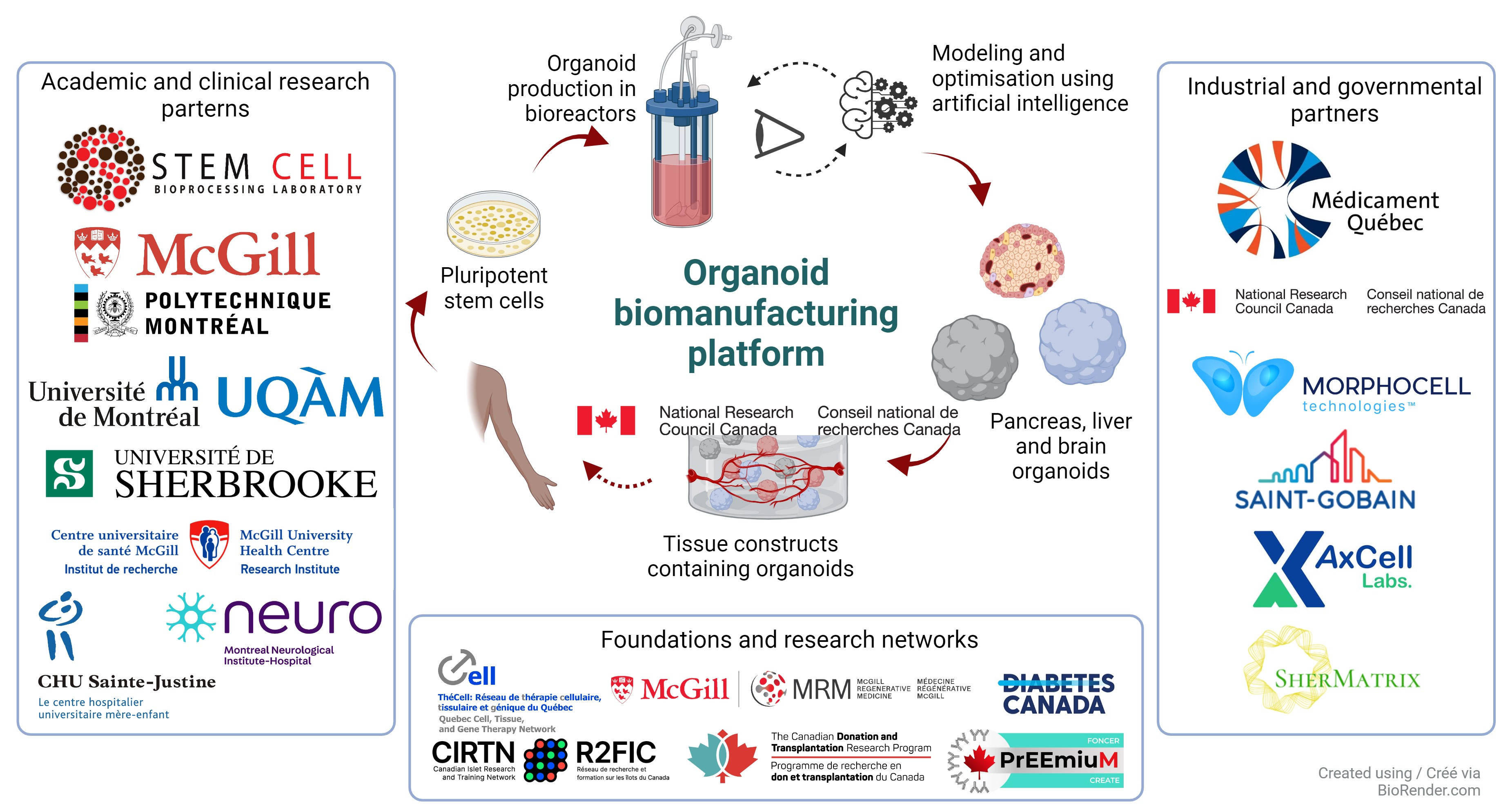
Teams involved in this project:
- Lead: Stem Cell Bioprocessing Laboratory (SCBL) of Prof. Corinne Hoesli, Department of Chemical Engineering, McGill University.
- Laboratory of Dr. Steven Paraskevas, Director of the MUHC Human Islet Transplant Laboratory, Department of Surgery, McGill University and Senior Scientist of the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre.
- Neuro-Early Drug Discovery Unit (EDDU) of Prof. Thomas Durcan, Department of Neurology Neurosurgery, McGill University.
- iPSCs Derived Liver Organoids Laboratory of Dr. Massimiliano Paganelli, CHU Sainte-Justine, Department of Pediatrics, Université de Montréal.
- Viral Vectors and Vaccines Bioprocessing Laboratory of Prof. Amine Kamen, Department of Bioengineering, McGill University.
- Systems Optimization Laboratory of Prof. Michael Kokkolaras, Department of Mechanical Engineering, McGill University.
- Optimization and Modelling Simulation Laboratory of Prof. Moncef Chioua, Department of Chemical Engineering, Polytechnique Montréal.
- Bioprocess Optimization Laboratory of Prof. Olivier Henry, Department of Biochemical Engineering, Polytechnique Montréal.
- Biomedical Materials Laboratory of Prof. Gregory De Crescenzo, Department of Chemical Engineering, Polytechnique Montréal.
- Laboratory of Prof. Francois Ouellet, Department of Biological Sciences, Université du Québec à Montréal.
- Laboratory of Prof. Diana Alison Averill, Department of Biological Sciences, Universite du Quebec a Montreal.
- Tissue engineering and Biomaterials Laboratory of Prof. Patrick Vermette, Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology, Université de Sherbrooke.
Out-of-province collaborator:
- UBC Diabetes Research Group of Prof. Timothy Kieffer, Department of Cellular and Physiological Sciences, University of British Columbia.
National Research Council of Canada:
Industrial collaborators and partners:
- Saint-Gobain Life Sciences, Solon (OH), USA.
- Morphocell Technologies, Montreal.
- SherMATRIX, Sherbrooke.
- Axcell Labs, Sherbrooke.
Networks directly supporting the project:
- Quebec Cell, Tissue, and Gene Therapy Network –ThéCell
- McGill Regenerative Medicine Network (MRM)
- Canadian Islet Research and Training Network (CIRTN)
- Canadian Donation and Transplantation Research Program (CDTRP)
- PrEEmium
Research Foundations:
Organizations supporting team members:
- CCRM
- CellCAN & CATTI
- Group for Research in Decision Analysis (GERAD)
- IVADO
- Cardiometabolic Health, Diabetes and Obesity Research Network (CMDO)
- Quebec Network for Research on Protein Function, Engineering, and Applications – PROTEO
- Quebec Centre for Advanced Materials (QCAM)
- Montreal Diabetes Research Center (MDRC)
To learn more, see the project description on the Médicament Québec website and the video below where Prof. Corinne Hoesli talks about the project in an event co-organized by Médicament Québec and Montreal InVivo (both in French).
